-
by admin
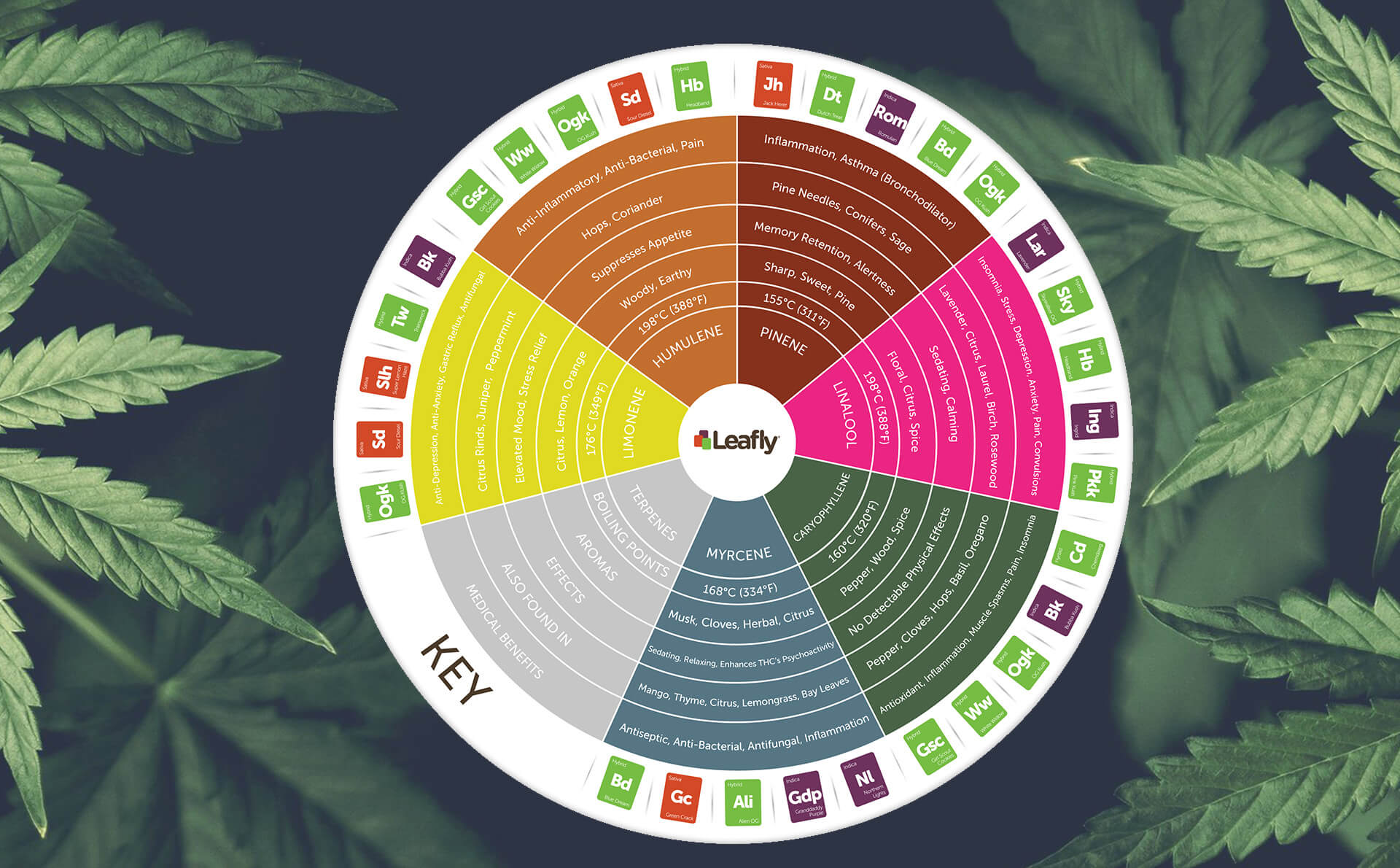
What are the main cannabinoids? As more people go on about the positive uses of cannabis, it seems like new cannabinoids keep popping up left and right. To clear up the confusion, we set
out to come up with a no-frills cannabinoid chart.
Cannabinoids are compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant. There are presently 104 variations [1] although this number keeps changing as scientists learn more and conduct better tests.
The two most popular cannabinoids—also known as the “main cannabinoids”—are THC and CBD. Of course, there are others that we’ll go over shortly.
Endocannabinoid system and decarboxylation.
There are two other terms you need to understand: the endocannabinoid system (ECS for short) and decarboxylation. If you didn’t already know that the body naturally produces endocannabinoids in the central nervous system, you’re on your way to understanding the cannabasics pretty quickly. Our bodies are constantly trying to reach homeostasis, or internal balance, therefore endocannabinoids bind to different receptors in the body to relieve pain and dodge stress. [2] Your body goes into homeostasis with the help of “feel good” hormones like dopamine and serotonin. When we use cannabinoids, the ECS functions even better. Now for the straightforward explanation of decarboxylation. Cannabinoids turn into different forms (aka synthesis) as they’re heated. The process of decarboxylation involves heating the raw form cannabinoids to lose carbon dioxide molecules.

From there, you have “activated” new cannabinoids like THC, CBD, and CBG. Most of the cannabinoids with more than three letters (CBGVA, for instance), are simply versions of the same cannabinoid with shorter chemical structures. [3] Of course, cannabis cultivators and processors all have their preferred method for producing “activated” cannabinoids. We promised, however, that this cannabinoid chart would be straightforward, so we’ll save cannabinoid extraction methods for another day. Here’s the list of different cannabinoids that originally brought you here:
- CBGa (Cannabigerolic acid)
Key features: CBGa is nicknamed the “mother of all cannabinoids” [4] because every other compound is formed from it. It’s non-psychoactive before decarboxylation, after which CBGa produces THC, CBD, CBC, and CBG.
Effects: Mood enhancer, pain reliever, appetite stimulant, antibacterial, neuroprotective [5] Potential medical benefits: Treatment for cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, depression, osteoporosis, Huntington’s, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
Key features: THC is the famous psychoactive cannabinoid. It is one of the two most present compounds found in cannabis.
THC is legal in some states but isn’t legal federally. Effects: Synonymous with feeling “high,” having the “munchies,” and getting “cotton mouth.” It increases appetite, makes people feel more sociable, and has anti-inflammatory properties.
Potential medical benefits: Common treatment for anxiety, insomnia, migraines, nausea, pain, and cancer.[6]
- CBD (Cannabidiol)
Key features: CBD is the non-psychoactive component in cannabis. It is legal in almost every state (all but three). It contains less than 0.3% THC in its hemp-derived form.
Effects: Supports mood enhancement, anti-inflammation, wakefulness, sleep Potential medical benefits: Treatment for anxiety, depression, insomnia, glaucoma, migraines [7] CBC (Cannabichromene)
Key features: CBC is non-intoxicating (if you’re picking up a pattern here it’s because THC is the only psychoactive cannabinoid). CBC works well with other cannabinoids in a synergetic relationship called the entourage effect.[8] Effects: Anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor properties Potential medical benefits: Treatment for breast cancer, acne, depression [9]
- CBN (Cannabinol)
Key features: CBN is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid that’s synthesized from aged THC. People often associate CBN with sleep because the THC enhances its drowsy effect. However, CBN doesn’t come from “old” cannabis as some people think. It’s the CBN/THC combination that makes people sleepy [10] (don’t miss out on the CBN supplement below to snooze more peacefully).
Effects: Mildly sedative, antibacterial, neuroprotectant, appetite stimulation
Potential medical benefits: Treatment for insomnia, arthritis, glaucoma, and ALS. This cannabinoid chart is a stepping stone to understanding the cannabasics. It isn’t a comprehensive list simply because we’re waiting on science to catch up and tell us more about the benefits of cannabinoids.
As you’ve learned from this cannabinoid chart, the cannabis plant has enormous potential and promise to work for all kinds of people. For this reason, cannabinoids are naturally generous and giving compounds to try for your health needs.
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5741114/
2. https://www.healthline.com/health/endocannabinoid-system#how-it-works
3. https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101/list-major-cannabinoids-cannabis-effects
4. https://wayofleaf.com/education/exploring-cbga
5. https://www.cannainsider.com/reviews/what-is-cbg/
6. https://www.healthline.com/health/cbd-vs-thc#at-a-glance
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3202504/
8. https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101/what-is-cannabichromene-cbc-cannabinoid
9. https://thoughtcloud.net/big-six-major-cannabinoids-effects/
10. https://www.leafly.com/news/science-tech/what-is-cbn-and-what-are-the-benefits-of-this-cannabinoid
SOURCE: https://sovereignty.co/cannabinoid-chart/